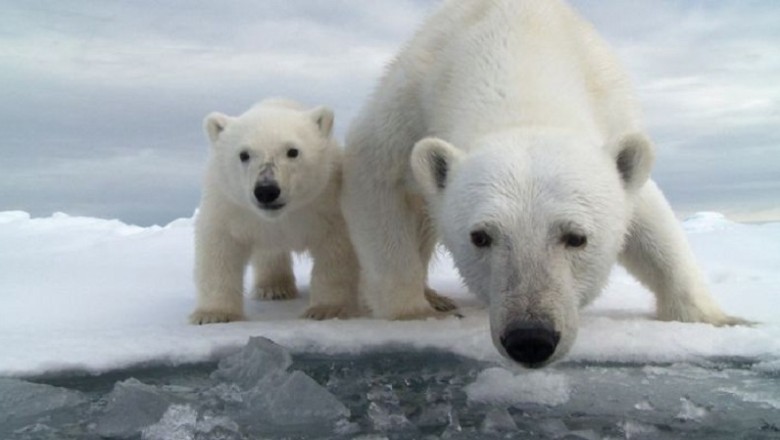
In the icy expanse of the Arctic, where the frost bites and the wind howls, there lives a creature that embodies the wild spirit of the frozen north—the polar bear. With their stark white fur and powerful frames, these magnificent mammals evoke awe and curiosity. Many might assume that just like their brown relatives, polar bears undergo a deep winter hibernation. However, as researchers have discovered, the reality is far more fascinating and complex.
The Ice and Fire of EvolutionPolar bears (Ursus maritimus) are the closest relatives of brown bears (Ursus arctos), having branched out from a common ancestor roughly 150,000 years ago—a mere blink in the evolutionary timeline. This proximity calls into question why one species hibernates while the other does not. Brown bears curl up in dens during the winter months, entering a prolonged state of hibernation marked by significant drops in body temperature and metabolic rate. In contrast, polar bears have crafted a lifestyle that defies the very notion of hibernation. They barely sleep—at least not in the way we typically define hibernation.
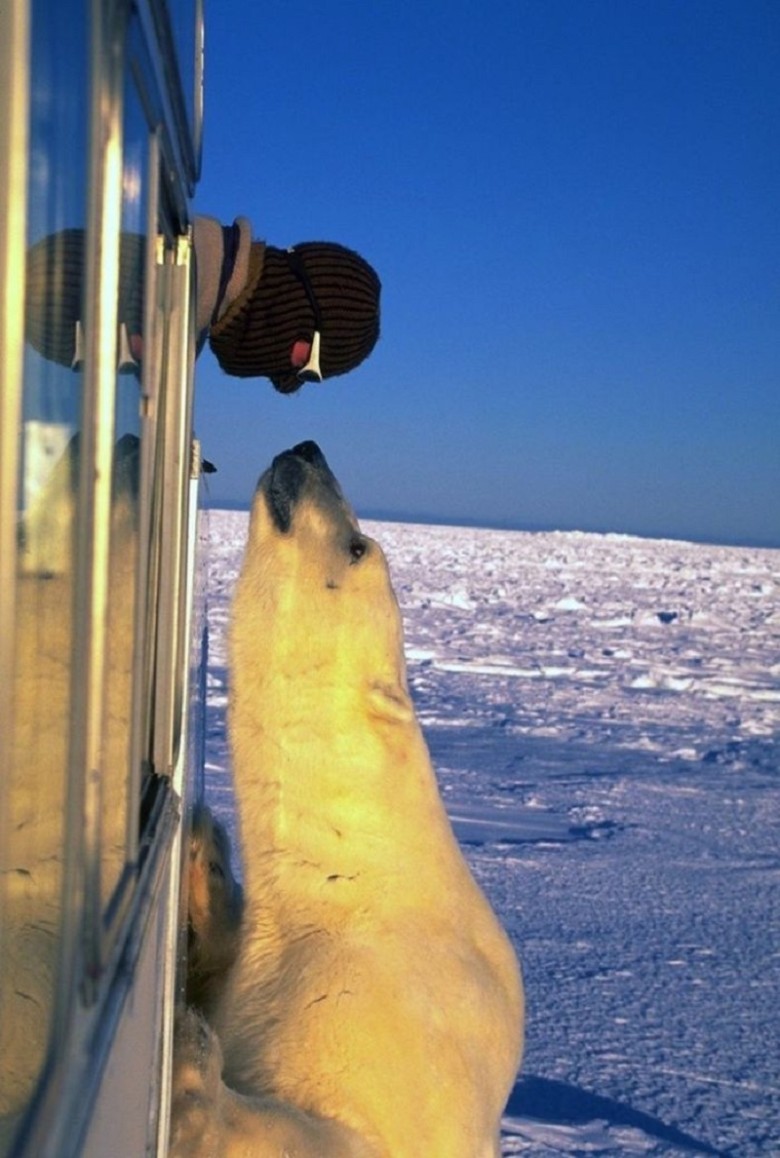

The reality is that polar bears primarily take short naps throughout the winter, much like they do in summer. Their unique habitat, characterized by full exposure to the harsh elements, makes those long periods of dormancy largely impractical. The Arctic is not for the faint of heart, and polar bears, created for this environment, continue their pursuit of food even in the depths of winter.
The Seal ConnectionAt the center of the polar bear's existence lies a singular and vital prey: seals. These marine mammals represent the primary diet for polar bears, who are adept hunters on ice. Using their impressive strength and keen instincts, polar bears hunt seals by lying in wait near holes in the ice. With a swipe of their formidable paws, they can snatch a seal in a heartbeat, feasting on the fat-rich meat that is essential for their survival.
Yet, the fragile Arctic environment holds another truth. As summer comes and the ice begins to melt, the hunting grounds that the polar bears rely on dwindle. The consequences are dire; by the end of summer, polar bears often face scarcity, unable to chase down seals or any other food source on land or sea, as most other Arctic animals can easily escape them. The bears may face months of hunger, further emphasizing the unique challenge they face in their field of white.
The Motherhood of SurvivalFor female polar bears, the challenge extends beyond mere survival; it's about nurturing the future generation. When the sea ice melts, pregnant females take to creating dens, far removed from the hunting grounds they usually thrive on. These dens are lifelines for their young—places of warmth and safety where babies can be born.
Polar bear cubs are born between November and January, usually when the mothers are deep into their hibernation-like state. Weighing less than a kilogram and completely blind, these tiny cubs require the utmost care. The female' s ability to create appropriate dens greatly affects the survival of these newborns. The mother prepares for this by gaining significant weight during the spring and summer months when hunting is plentiful. Upon mating in the spring, pregnant females consume an incredible amount of food, often doubling their weight by autumn.
Interestingly, the development of the embryos of polar bears pauses immediately after mating, entering a state known as embryonic diapause. During this period, their bodies adapt to the conditions around them, allowing the cubs to develop at the most suitable time. In harsh Arctic conditions, this ensures cubs are born at a time when their mother can ensure their survival.
The Genius of AdaptationPolar bears have developed incredible adaptations to thrive in an environment that would spell disaster for many other creatures. While being in a state of winter sleep, the females do not eat, drink, or even eliminate waste. Miraculously, these mothers accumulate the necessary nutrients before going into the den, supporting their needs while also providing essential nourishment for their young.
One remarkable adaptation allows polar bears to undergo long fasting periods with minimal waste. When faced with prolonged hunger, the concentration of urea—an indicator of metabolic activity—declines in their blood. This change enables them to conserve energy and water consumption, as their bodies can utilize urea to synthesize essential amino acids and proteins. Remarkably, they achieve this while maintaining their muscle and bone mass during periods of inactivity.
In sharp contrast, brown bears experience significant loss of muscle and bone mass during their winter hibernation. In fact, polar bears demonstrate a unique ability to burn fat more effectively than other bear species. Their selective metabolic approach helps them navigate the unforgiving environment, ensuring they remain well-equipped for when food sources become available again.
The Struggle for SurvivalDespite their adaptations, polar bears are not immune to the looming threats of climate change. As the Arctic ice continues to diminish at an alarming rate, their hunting grounds are compromised. Each summer that passes leads to increased uncertainty about their future, pushing them closer to the brink of endangerment.
While visiting the icy realm of the polar bear, one cannot help but be struck by their majestic nature and extraordinary ability to endure harsh conditions. However, it is sobering to realize that the very environment that shapes their existence is disappearing. We find ourselves challenged to reflect on the role we play in protecting these magnificent creatures for generations to come.
A Call to ActionAs human beings share their stories with the Arctic's native wildlife, our responsibilities extend beyond emotional attachment; we must take action to ensure their survival. Conserving the fragile Arctic habitat is paramount. Supporting initiatives that combat climate change is a significant first step. Each person's efforts—no matter how small—can make a wide-reaching impact when we band together for a common cause.
We can also advocate for wildlife protection policies that address the needs of polar bear populations. Educating others about the realities of polar bear life can foster a sense of connection and responsibility, enabling people to understand the stakes involved in their survival.
Wildlife organizations, schools, community groups, and individuals should strive to maintain awareness and promote actions that protect not only polar bears but also the ecosystems they inhabit. Learning about sustainability, emphasizing the importance of biodiversity, and understanding the interconnectedness of all living beings can spark the change needed to ensure the future of these regal creatures.
Our Shared StoryThe journey of the polar bear offers more than just scientific interest; it serves as a powerful narrative about our connection to nature and the responsibilities we carry. As these bears navigate the icy wilderness, their lives reflect resilience, adaptation, and a fierce determination to survive.
Let us not forget that the actions we take today ripple into the future. By preserving habitats and respecting the delicate ecosystems that allow polar bears to thrive, we honor their spirit and ensure that the story of these iconic beings continues.
As we gaze upon the shimmering ice and the majestic bears that roam it, we are reminded that our world holds powerful stories—stories of life, struggle, and survival that weave together the thread of existence. The polar bear stands as a symbol of endurance, resilience, and familial bonds that are worth preserving. Together, may we stand vigilant in our commitment to protecting these remarkable creatures and the fragile realms they inhabit, for they share our planet and its future.